Science & Technology
Success of RNA therapeutics requires optimal delivery to the site of disease

-
High delivery efficiency to nose and lung
-
Safe and well tolerated in human epithelium
-
Rapid uptake and cellular retention
-
Aerostability demonstrated with conventional nasal sprays and nebulizers
-
Payloads including RNA, DNA and small molecules
-
Low immunogenicity
-
Phase 1 ready nasal and inhaled formulations
Delivery of RNA Therapeutics
Critical success requirements for delivery
-
High transfection efficiency (endosomal uptake and escape)
-
Formulation optimized for lung retention
-
Formulation can be applied to a diverse and broad range of payloads
-
Formulation tolerates shear stress post-aerosolization
-
Good tolerability and safety for acute and chronic applications
NEED™ proprietary non-LNP nano-emulsion platform overcomes the limitations of LNPs
Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP) Platforms |
RIGImmune Nano-Emulsion |
Ionized LNP cationic lipids interacts with endosomal membranes which destabilizes lipid bilayers resulting in membrane disruption and endosomal escape of the LNP into the cytoplasm |
Surfactant based delivery system promoting endosomal escape over a wide range of RNA payloads. Suitable for delivery to other epithelial surfaces including eye and skin. |
Less than 2% of RNA-based LNPs that are taken up by the cell release their cargo into the cytosol. |
Safe and well tolerated in human epithelium (non-endolytic nano emulsion) resulting in rapid uptake and cellular retention |
Cholesterol and the PEG-lipid in LNPs contribute to the stability of the drug product while the phospholipid required for fusogenicity |
High transfection efficiency (nano-emulsion greater than ~10 fold versus buffer only) |
LNPs are directly toxic to lung epithelium and can induce activation of the immune system resulting in complement activation-related pseudo allergy (CARPA), an acute immunological response |
GRAS excipients only with long experience of human safety with respiratory tract delivery |
LNPs are subject to shear stress after aerosol delivery and unable to maintain particle integrity |
Maintain particle integrity after nasal spray and aerosol delivery |
Predominantly deliver mRNA cargo to liver and spleen |
Phase 1 ready nasal, inhaled and subcutaneous formulations |
Broad Therapeutic Applications
The potential of RIGImmune’s NEED™ Delivery Platform extends far beyond respiratory therapies. This versatile platform is poised to transform treatment paradigms across various medical fields where targeted nucleic acid delivery is crucial. Our ongoing research and development initiatives are dedicated to unlocking the full capabilities of the NEED™ platform. The platform is adept at handling a diverse range of payloads including RNA, mRNA, and DNA, demonstrating its capability to cater to a broad spectrum of therapeutic needs.

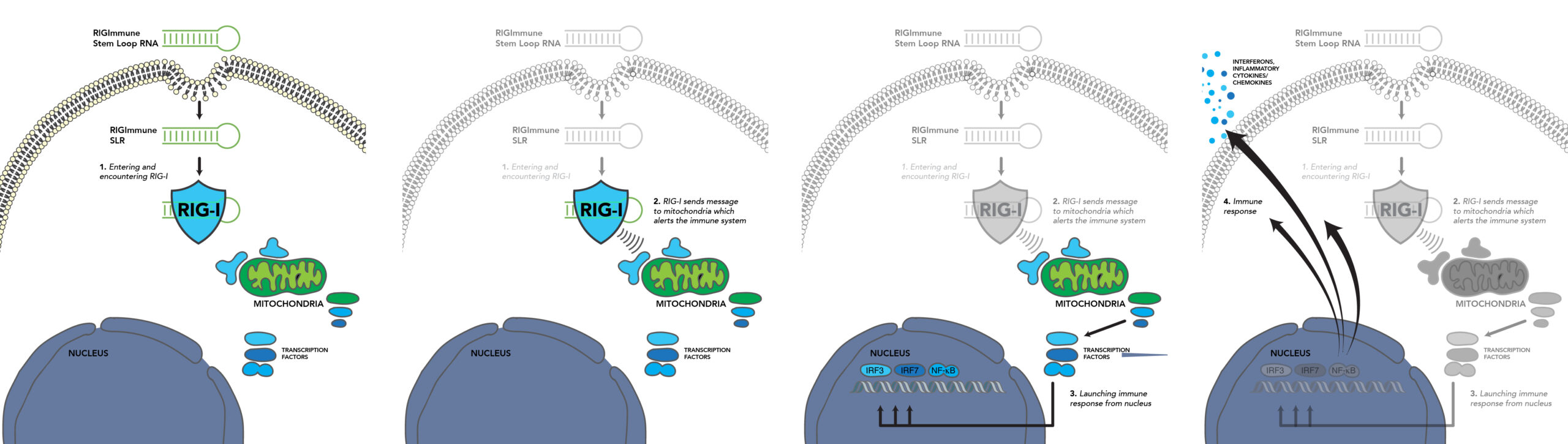
RIG-101 & RIG-I Pathway
The lead product development candidate, RIG-101, a RIG-I agonist formulated with the NEED™ technology and delivered by the intranasal (IN) route, is advancing through IND-enabling activities for a clinical program designed for the prevention of asthma exacerbations caused by viral respiratory infections in at-risk patent populations. RIG-101 is specifically designed to prevent infections caused by a broad range of RNA viruses including Human Rhinovirus (HRV), RSV, influenza, and SARS-CoV-2. IN NEED™ formulation delivers RIG-101 directly to the site of replication in the nasopharynx, thus preventing viral infection and providing a pan-viral profile.
RIG-I activation by RIG-101 triggers and increases the speed of a multi-faceted immune response and preclinical data has shown RIG-101 to be effective in prevention of asthma exacerbations caused by existing and emerging RNA viruses, most notably HRV.